Healthcare with Confidence
After clinical trials in the United States, Europe and United Kingdom, Health Ministry of Israel has approved a new immunotherapy – CAR-T therapy for the treatment of blood cancer and lymphoma.
Close cooperation between Israeli and American researchers allowed to find out the best appropriate solution for patients who come for treatment in Israel.
Results of the research group at the National Cancer Institute and other American and European cancer centers showed complete cure of more than 70% of patients with refractory and recurrent leukemia. Currently CAR-T therapy is the most modern method of immunotherapy.
What is CAR T cells therapy?
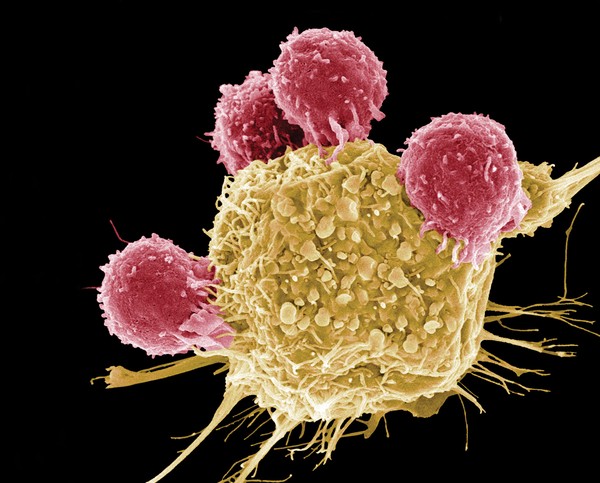
CAR T is considered the cutting edge of the most innovative and revolutionary treatments in hematological malignancies. This is a type of immunotherapy where the patient’s own T-cells (white blood cells) kill cancer cells.
White blood cells (lymphocytes) of type T (T Cell) belong to the immune system and their role is to protect the body from pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, and from the development of cancerous tumors.
Cancer cells “know” how to suppress the T cells activity and escape from them. Therefore, immune system should be directed against the tumor. With CAR T treatment immune system identify the cancer cells successfully and destroy them. Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR-T does just that.
How CAR-T therapy works
Cells of the immune system are collected from the patient, and T cells are isolated from them. The cells are sent to the laboratory, where they are genetically modified so that they express a special receptor to identify cancer cells. Then a large amount of transgenic T cells are grown in the laboratory, and after this injected into the patient. The receptor on the T cells binds to a specific protein that is found in large quantities on the cancer cells. Binding the receptor to the protein attaches the T cells to the cancer cells and activates them to attack. Shortly, the cells of the immune system acquire a sophisticated weapon that guides them to act against the cancer cells, recognizing and destroing the tumor in the body.
After the “treatment” in the laboratory, the upgraded cells are given to the patient by infusion, which usually takes less than an hour. CAR T is a one-time treatment.
Before the infusion, the patient receives chemotherapy drugs in order to suppress his own immune system and thus give priority to the engineered cells to thrive and multiply in the body and attack the tumor. It may be Fludarabine and Cyclophosphamide.
Who is a candidate for CAR-T therapy? What kind of cancer can be treated with CAR-T therapy?
- Children and young patients (up to 25 years) for treatment:
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Refractory leukemia
- Recurrent leukemia
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Multiple myeloma
- Elderly patients:
- B-cell lymphoma
What are the stages of CAR-T treatment or Kymriah?
- Using apheresis, a small amount of lymphocytes is extracted from a patient’s blood sample.
- The collected T-cells are sent for preparation to a special certified laboratory.
- In the laboratory genetic engineers directly modify lymphocytes and attach to a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). In this way, T-cells is trained to eliminate cancer cells. The preparation process itself may take two to three weeks.
- For successful absorption of grown CAR T-cells in the body, preliminary short chemotherapy is performed.
- Within an hour, T-cells infused back by intravenous drip. After the infusion, the patient remains hospitalized in Medical center for about 20 days – up to 1 month to monitor the treatment course.
How do you feel after the treatment?
The chemotherapy drugs given before the infusion mainly suppress the lymphatic system, but they cause a temporary decrease in blood counts and are accompanied by the usual side effects, such as fever, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea and rash.
Side effects of CAR-T therapy (kymriah) treatment
40-60% have side effects from treatment that are reversible. They may include a cold fever-like symptoms:
- chils;
- headache;
- dyspnea;
- lowering blood pressure;
- seizures.
In exceptional cases, some side effects require treatment in the intensive care unit.
CAR-T Success rate in Israel
CAR T success rate in Israel is 60%-70%, depending on the type of disease, its severity and the patient’s general condition before treatment and hospitalization.
⇒ Please see one of our Patients Review about CAR T treatment in Israel
What are the possible complications?
A temporary drop in blood count that can lead to anemia, bruising or bleeding (usually minor), and infections; Cytokine Release Syndrome – a systemic inflammatory response of the body to cytokines (proteins) that are released as a result of the attack of the CAR-T cells against the tumor. The reaction may cause fever, low blood pressure and more; Neurological symptoms, such as headaches, confusion and blurriness, lack of mental clarity and slurred speech.
Where can you get CAR-T therapy in Israel?
At the moment leukemia treatment is carried out only in a few medical centers in the world, mainly in the United States and Israel – at Sheba Hospital and Ichilov Medical Centers. These centers include not only medical buildings, but also research laboratories, where they are permanently studying and improving cancer treatment methods.
CAR-T treatment can be performed at the Institute of Hematology, Sourasky Medical Center (Ichilov), Tel-Aviv under the guidance of experienced hematologists – prof. Ella Naparstek, prof. Irit Avivi as well as in the hemato-oncology department at Sheba Medical Center under the guidance of prof. Arnon Nagler and dr. Elad Jacoby.
These medical centers have a doctors team who specializes in CAR-T therapy. They are experienced in the treatment process, and also reduce the risk of side effects.
Leukemia can be a devastating disease, especially in children. But we believe that the solution for this issue lies in advanced medicine and quality service.
Please contact us for free consultation with our specialists in CAR-T Treatment. You will be consulted about whether this treatment is an option for you.
You will get a program and costs for the procedure.
⇒ To consult with Doctor for Leukemia Treatment
⇒ To consult with Doctor for Lymphoma Treatment
⇒ To consult with Doctor for Multiple Myeloma Treatment
⇒ All leading hematologists of Israel from latest Forbes List
If you have questions about the Hematology cancer treatment and CAR-T therapy, or if you want to make an appointment about your disease with the leading hematologists or oncologists in Israel, contact via chat, form or by phone, Whatsapp, Viber.