Healthcare with Confidence
Skin cancer is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells with damaged DNA structure. These cells proliferate and form a cancerous tumor.
Israeli cancer physicians have a lot of experience in treating all types of skin cancer. Thanks to timely diagnosis and proper treatment, most types of skin cancer are not dangerous.
The most aggressive type of skin cancer is melanoma, which metastasizes to other organs in its advanced stages. But even in this case, the chances for recovery are very high, thanks to advanced methods of melanoma treatment in Israel.

World known Israeli oncologist, specialist in Melanoma and Skin Cancer
Prof. Jacob Schachter – Head of the Ella Lamelbaum Institute for Melanoma and Immunooncology at Sheba Academic Medical Center, Chaim Sheba Hospital, Israel.Deputy Director of Oncology Department of Chaim Sheba Hospital. Appointment online.
The main types of skin cancer:
♦ Squamous Cell Carcinoma
♦ Basal Cell Carcinoma (basalioma)
♦ Actinic Keratosis
♦ Dysplastic Nevi (atypical mole)
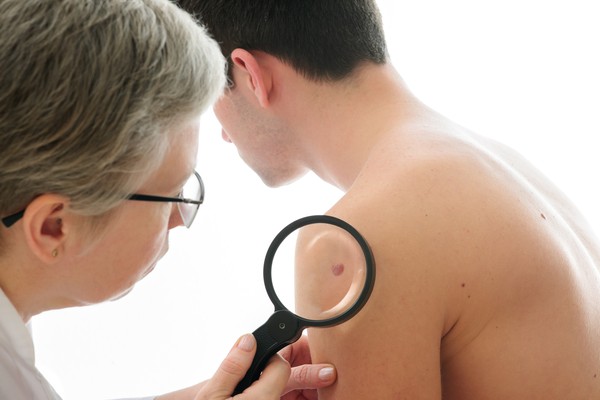
The first step toward the effective treatment is a correct diagnosis.
Skin cancer diagnostics:
⇒ Digital mapping of skin – early diagnosis of melanoma
♦ Blood test
♦ PET-CT
♦ Biopsy and histological examination
♦ Oncologist consultancy
♦ Surgeon consultation (in case of indications for tumor resection)
Diagnosis in Israel usually lasts about 4-5 days.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) – this kind of skin cancer accounts for about 20% of all cases. Such tumor usually grows slowly, but it may be more aggressive and sometimes it may spread metastases. Squamous cell carcinoma looks like an unhealed wound, a lump on the skin, or a scaly area. In some cases, squamous cell carcinoma can grow very quickly and cause significant local injury. Squamous cell carcinoma is most aggressive when it develops on the lip and mucous of the oral cavity and tongue. This phenomenon is more common in smokers and requires alertness and referral to a doctor in all cases when there is a non-healing wound in the mouth or on the lips. The risk factors for the development of squamous cell carcinoma, as well as for basal cell carcinoma, are light skin, exposure to the sun, and elder age, usually older than 60 years. As with basal cell carcinoma, different types of treatment are used for squamous cell carcinoma, starting from ointments and ending with surgery (Mohs surgery), radiation therapy and, in extreme cases, chemotherapy.
Basal cell carcinoma – is an abnormal, uncontrolled growth of damaged basal cells, which are in the deepest layer of the epidermis (the top layer of skin). Basal cell carcinoma often looks like an open wound, red spot, pink blotch, shiny bump or scar. Typically basalioma does not metastasize to other organs. Metastatic process of this tumor is very rare. After the dermatoscope examination basal cell carcinoma diagnosis should be confirmed by histological study in laboratory. If tumor cells are present, urgent treatment is necessary.
Dysplastic nevi (atypical mole) is formed of melanocytic cells and, in some cases, it is transformed into melanoma. This mostly depends on the genetic predisposition of the patient. Dysplastic nevus diagnosis should be done with dermatoscope and histological studies. This diagnosis should be a subject for immediate surgical removal. In the future, patients diagnosed with dysplastic nevi are at increased risk of developing melanoma, and it requires an annual regular inspection by dermatologist.
Actinic keratosis, also known as solar keratosis, is a solid lesion that appears mostly on the head, face, ears, lips, back of the hands and forearms, shoulders, neck, or any other parts of the body often exposed to the sun. Keratosis is a precursor to skin cancer and it can transform into an aggressive form of cancer, so once detected it must be treated immediately. Such disease is diagnosed with the dermatoscope, which allows a dermatologist to determine this type of cells at the microscopic level.
Treatment method is determined based on the type, size, location, and depth of penetration of the tumor, patient’s age and general condition.
Surgical excision. In this case surgeon removes the minimal amount of tissue. This minimally invasive procedure is easy to stand and it leaves scars of small sizes, which disappear with time. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis in the doctor’s office and it does not require hospitalization.
Mohs micrographic surgery. The essence of this operation is to remove a thin layer of skin in one micrographic excision under control. Excision is terminated when a precision microscope no longer detects skin cancer cells. This method can detect cancer cells in the layers of skin, and at the same time to preserve as much healthy tissue as possible. Staining is used to identify cancer cells. In such immunocytochemical or immunohistochemical staining dyes are absorbed predominantly by skin pigment cells (melanocytes) of which melanoma is formed, allowing them to be seen clearly under the microscope.
Radiotherapy. In some cases, basal cell carcinoma may be destroyed when it is exposed to X-rays, without the need for surgery. Total destruction of the lesion is usually achieved by few treatments per week for several weeks. Radiation treatment is used in cases where there is a contraindication to surgical methods, such as the elderly age or patient’s general condition. This method has a 90 percent cure rate, but entails some complications in the form of long-term cosmetic problems.
Cryosurgery. Method of freezing the tumor tissue with liquid nitrogen is used less frequently than all of the above methods, due to its lower efficiency. It is used only by the physician and usually in patients with bleeding disorders or intolerance to anesthesia.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT). Laser treatment. These methods are used as a secondary therapy when other methods are unsuccessful, as well as in those with recurrent disease. In Israel such treatment is not widely used due to its lower efficiency.
Immunotherapy. Immunological and biological treatment is used mostly in case of melanoma treatment.
Chemotherapy. In extremely rare cases of metastatic basal cell carcinoma or locally advanced basal cell carcinoma, when this type of cancer becomes life-threatening, chemotherapy may be applied. But it is used in cases when other methods (e.g., surgery or radiation treatment) cannot be used.
When keratosis was diagnosed usually special creams and solutions are applied to diseased skin for several weeks. This may be interferon stimulating drugs, non-steroid anti inflammatory agents, in some cases, a laser and photodynamic therapy.
The treatment method is determined individually for each patient by the physician, taking into account complete clinical picture, aggressiveness of the tumor, sensitivity to medicines and general condition of the patient. Treatment can be one of the above methods or it may combine several techniques.



 Dr. Zipel Dov – Head of the Oncological Surgery unit, Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer.
Dr. Zipel Dov – Head of the Oncological Surgery unit, Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer.
